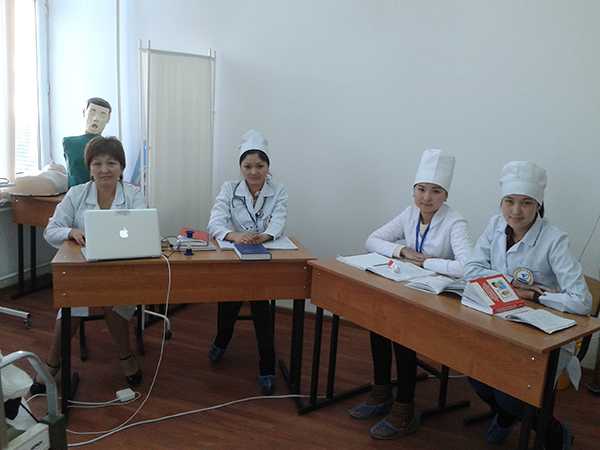
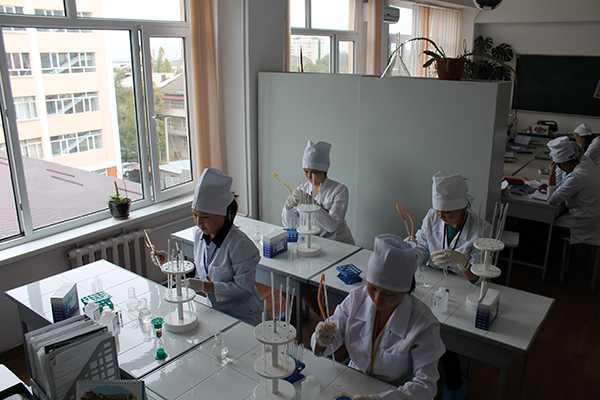
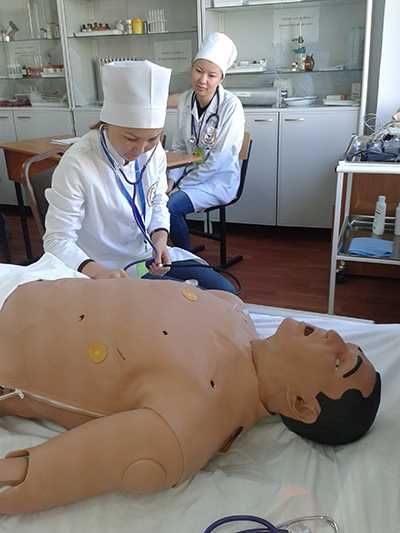
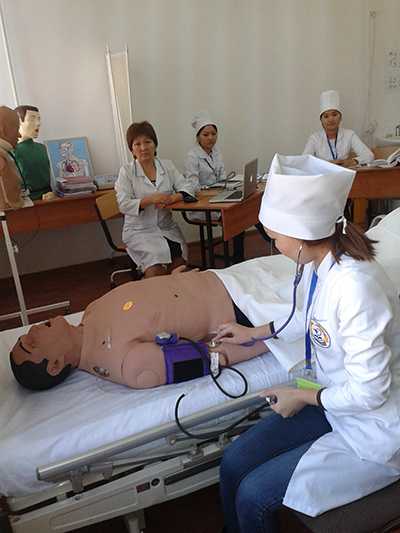
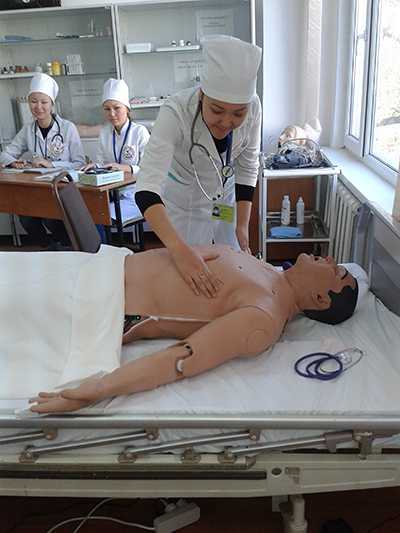
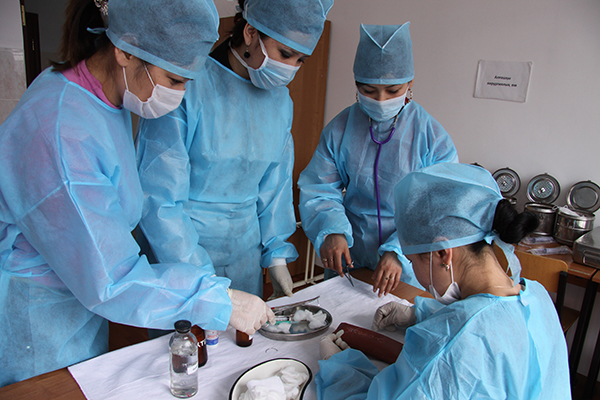
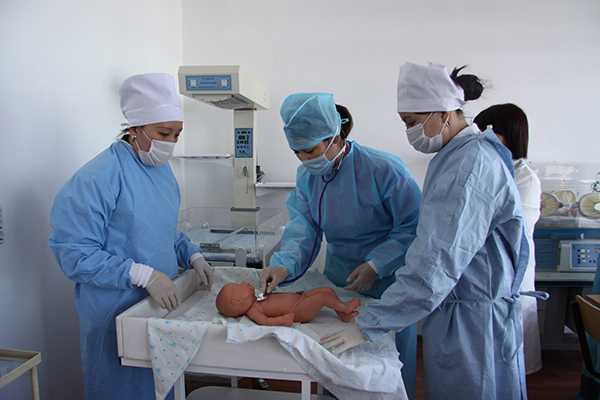
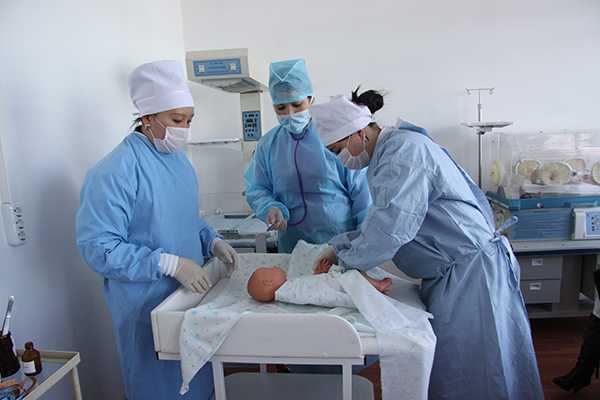
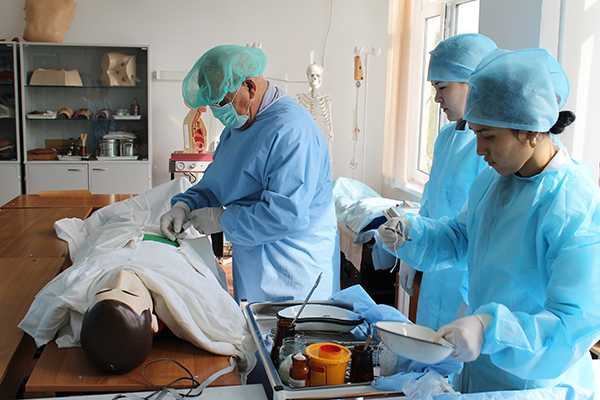
Center for monitoring practical skills
The structure of the Monitoring Center (two blocks) includes preclinical practice rooms and laboratories.
All rooms are equipped with modern simulators, mannequins, medical equipment and instruments, audio-video equipment with a network connection. The installed video camera and a sensitive microphone allow you to observe and hear everything that happens in the educational process. All information is sent to the operator’s room, where it is monitored, stored, and the recording is reproduced during the debriefing of the lesson.
The purpose of the quality monitoring center is to assess the quality of the provision of educational services in professional practice and to identify the level of practical skills and abilities of students. Providing a safe, reliable educational environment for teaching clinical skills.
The organization of a center for the development of professional skills takes into account an integrated approach to practical activities and provides for specially designed training programs using high-tech simulators, simulators, the introduction of a knowledge and skills assessment system: The first step is to conduct manipulations on virtual simulators, practice practical skills on dummies. The second step is preparation for practice, working with standardized patients.
One of the tasks of the Concept is the further introduction of active teaching methods and the expansion of the use of simulation technologies in clinical education, the introduction of standardized and simulation patients into practice.
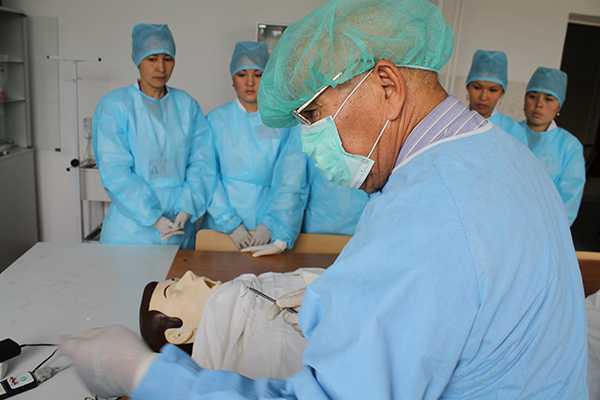
The JV methodology has been introduced since 2011. For the further implementation of the tasks set in the Quality Monitoring Center at preclinical practical classes, training is carried out using a modern sample of the Meti technology of the Metiman and BabySim computer simulator robots. The robot simulator has not only the ability to assess user actions, but also parameters that simulate violations of the functions of organs and systems, contribute to a more effective use of new technologies, since they include programmed scenarios. Students have the opportunity to master the skills of examining patients, study clinical psychology, deontology, as well as conduct individual and team actions in case of emergency conditions available in the clinic of internal diseases. Classes are held in a specially equipped room, that is, the “virtual therapy room” fully imitates a real clinical unit.
Simulation training is based on the principle “I learn by doing, only repeated repetition of various situations and analysis of the correctness of actions in them lead to the formation of clinical experience acquired in an artificially created simulation environment.
The advantages of using the simulation method in practical training:
- In the course of mastering practical skills, neither the patient nor the student is at risk.
- Unlimited number of repetitions and duration of interventions practicing.
- The duration of the educational process is not limited, the schedule does not depend on the patient’s daily regimen.
- Both common diseases and conditions and rare types of pathologies are demonstrated and practiced.
- Stress is mitigated with the first real interventions.
- The possibility of an objective assessment of the level of practical training is expanding
- Learning efficiency – continuous accumulation of skills and experience is ensured in a short period of time.
- Ensuring safety – does not create inconvenience, discomfort and does not pose potential harm to real patients.
- Corrective Advantage – The student receives immediate feedback and has the ability to repeat in case of error.
The effectiveness of simulation techniques:
- provides a dynamic educational resource,
- creates a safe supportive environment for practical medical education,
- promotes the development of clinical thinking,
- acquiring basic skills through regular training,
- contributes to the survival of practical skills and abilities.
The tasks of monitoring the provision of educational services for vocational training are:
- Assistance in improving the quality of the provision of educational services in professional practice and identifying the level of practical skills and abilities of students
- participation in the modernization of the educational process in accordance with modern requirements
- formation of skills of independent and self-directed learning of students
- organization and implementation of active teaching methods, using mannequins, models, dummies, standardized patients in teaching and teaching clinical skills.
- continuous, dynamic monitoring of the quality of organization and conduct of professional practices, obtaining operational and objective information;
- survey of the dynamics of the provision of educational services provided by teachers;
- identifying the real level of qualifications of teaching staff, their readiness for professional practice, solving innovative problems;
- identifying the level of mastering practical skills and abilities among students, advanced training of secondary medical and pharmaceutical personnel;
- analysis of the quality of preparedness of students for professional activities and the possibility, on this basis, of adjusting the curriculum of professional practice.
Monitoring center functions
- Control over the timely conduct of practical classes in accordance with the schedule of the educational process.
- Control over the implementation of working curricula and professional practice programs conducted in the center.
- Control over the quality of the provision of educational services for professional practice by teachers
- Analysis of the level of development of the material and technical base of the classrooms and laboratories of the center.
- Monitoring the quality of training and teaching clinical skills, using modern technologies and methods
- Analysis of the security of the educational process in professional practice with educational and methodological materials, letters.
- Conducting current, intermediate control and final certification of graduates.
- Preparing a schedule for working off missed practical classes and monitoring its implementation.
- Providing advice to students in working out missed classes